Lesson:
Ultrasonic sensor
What is an ultrasonic sensor? Sensors that can detect something in their path or some obstruction. How do they work? Ultrasonic sensors work by sending out a sound wave at a frequency above the range of human hearing. The sensor can determine the distance from a target by recording the time that it takes for the sound wave to bounce back towards the sensor’s microphone.
Hands On:
Ultrasonic movement detection that is modulated by LED with a PWM signal
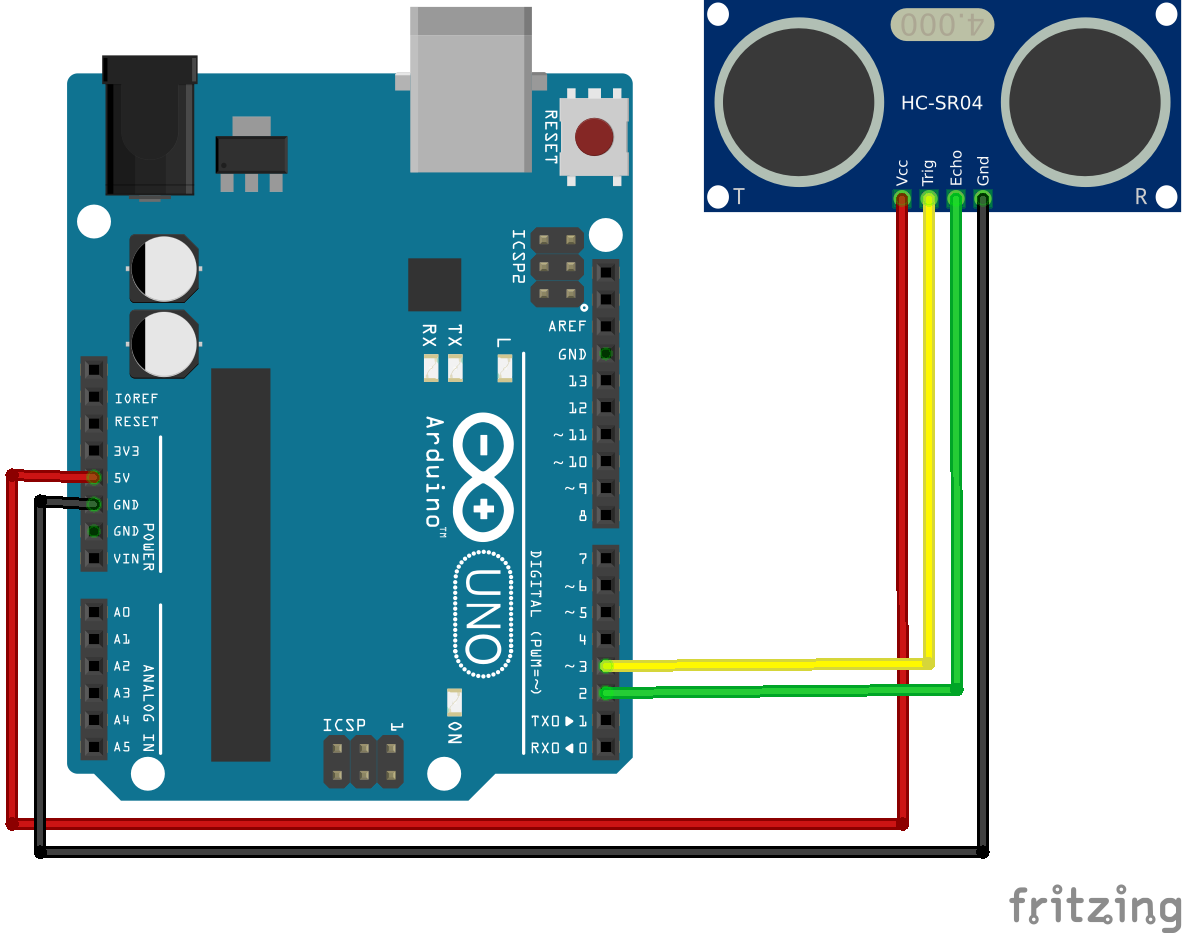
- VCC pin is power, connecting to 5V on the Arduino
- GND pin connects to the GND pin on the Arduino board
- The Trig pin is used to trigger an ultrasonic wave, and connects to a digital pin on the board
- The Echo pin is the pin that goes high for a period of time which will be equal to the time that it takes for the wave to return to the sensor. This also connects to a digital pin on the Arduino board.
Advanced activity: Check the code below. It reads a distance from the ultrasonic sensor and displays it on the monitor. Try running it.
Your task is to design a game in which you are to get the ultrasonic sensor reading as close to a goal distance as possible. The goal distance must be randomly picked in a reasonable range, and you can use the reading distance code below as the base of your game.
Students should start with this code below:
// defines variables
long duration; // variable for the duration of sound wave travel
int distance; // variable for the distance measurement
void setup() {
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); // Sets the trigPin as an OUTPUT
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); // Sets the echoPin as an INPUT
Serial.begin(9600); // // Serial Communication is starting with 9600 of baudrate speed
Serial.println("Ultrasonic Sensor HC-SR04 Test"); // print some text in Serial Monitor
Serial.println("with Arduino UNO R3");
}
void loop() {
// Clears the trigPin condition
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
// Sets the trigPin HIGH (ACTIVE) for 10 microseconds
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
// Reads the echoPin, returns the sound wave travel time in microseconds
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH);
// Calculating the distance
distance = duration * 0.034 / 2; // Speed of sound wave divided by 2 (go and back)
// Displays the distance on the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println(" cm");
}
Final Behavior outline:
-
Tells player a round is starting and the round number
-
Generate a random distance and inform the player of the distance. Make sure to use
randomSeed()on an analog pin. Userandom()with two arguments to generate random numbers in a range- Example:
randomSeed(some_analog_pin); (in setup) random(0, 50) (in loop): generates a random number in the range 0-50
- Example:
-
Provide a 3, 2, 1 countdown for the player to place their hand in place attempting to match the goal distance (use delay function)
-
Provide the result and how far off the player was
-
Start the next round (it is a loop so this should automatically happen)